Reducing Risk of Diabetic Foot Complications with Smart Footwear and Remote Patient Monitoring
According to the World Health Organization, over 422 million people suffer from diabetes. Diabetes is an emergency of epidemic proportions, and diabetic foot complications have one of the most painful effects—every 20 seconds, someone in the world loses a lower limb due to diabetes. The total worldwide cost of diabetic limb complications is estimated to be $46 billion, and in the US, direct costs associated with these complications exceed the cost of each of the five most expensive cancers. After an amputation, the patient’s life expectancy is five years.
From the staggering numbers above, Remote Patient Monitoring and patient adherence monitoring via connected footwear will play a major role in the future of diabetic care. As one of the most innovative applications of IoT in healthcare, remotely monitoring patients is essential to ensuring effective treatment, improving patient care, and reducing hospital readmission rates. This requires data to flow smoothly from patient to clinician, and from clinician to clinician. However, the currently siloed healthcare industry with data stored on-premises and lack of interoperability among these on-premises systems makes it difficult for clinicians to access data in a timely manner to proactively treat patients. And when diabetic foot ulcers can potentially cause the loss of limbs, the stakes are remarkably high for all parties involved.
Making real-world remote patient monitoring data accessible
One of the biggest challenges in treating diabetic foot ulcers is the ability to monitor the patient’s progress when they are outside of the hospital. The lack of availability and inaccessibility of this quantified data prevents clinicians from collaborating with patients to ensure they adhere to the clinical recommendations, thus reducing the effectiveness of treatment and care. Our innovative diabetic footwear will enable the creation of a new category of solutions for podiatrists, which will not only provide valuable feedback to and from patients but also supply clinicians with the patient’s compliance and usage patterns for healing diabetic foot ulcers, supporting the goal of reducing the risk of occurrence.
Sensoria’s diabetic footwear is a wonderful example of how Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) health data can be leveraged to improve clinical workflows and process valuable data to support both patient and clinician while making individualized care plans. IoMT health data can be ingested from the Sensoria footwear and compiled to attain a valuable holistic view of a patient’s at-home care, knowledge of self-care, and care plan compliance. The IoMT health data coming from the footwear can be de-identified, compiled, and stored in Microsoft HIPAA compliant cloud infrastructure.
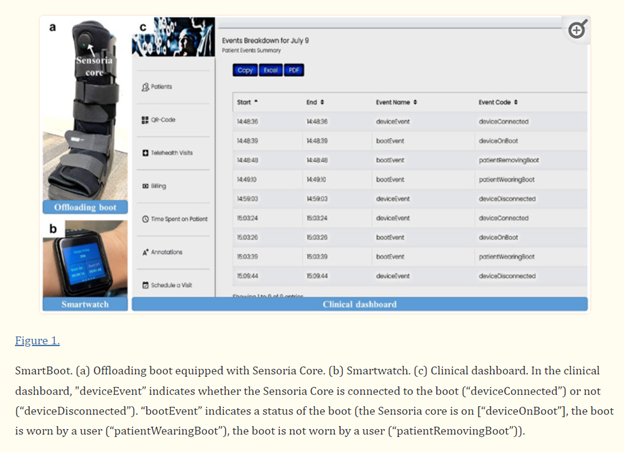
Powered by Sensoria Core, a wearable sensor platform that is modular, self-contained, and fully integrated to provide highly accurate data, the Sensoria Diabetic Foot Ulcer Boot can measure whether the patient is wearing the boot, their level of activity, and adherence to the recommended clinician protocol.
The clinician dashboard provided by the Sensoria Diabetic Foot Ulcer Boot offers a holistic view of their patient population. The dashboard is color-coded so that clinicians know which patients are at most risk due to non-adherence. In these cases, there is an escalation of care that can be identified, and the boot can be made irremovable.
Sensoria Health is excited to be a pioneer of this effort with global diabetic footwear partners such as Defender Operations.
A very recent study “Smart Offloading Boot System for Remote Patient Monitoring: Toward Adherence Reinforcement and Proper Physical Activity Prescription for Diabetic Foot Ulcer Patients” published in the Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology concluded that our Sensoria smart boot is the first smart offloading system that enables remote patient monitoring and real-time adherence and activity reporting. Future studies warrant clinical validation of real-time non-adherence alerting to improve wound healing outcomes in people with diabetic foot ulcers.
The Sensoria Powered Smart Offloading Boot System
The figure below shows an Ossur DH Smart Boot consisting of: (1) a mechanical offloading boot equipped with Sensoria Core microelectronics; (2) a smartwatch with dedicated patient monitoring app and 4G LTE Internet of Things (IoT) sim card enabled; and (3) a cloud-based clinical dashboard. The offloading boot is a commercially available removable knee-high footwear equipped with two Velcro straps for the foot and three Velcro straps for the lower leg. The Sensoria Core microelectronics include a microcontroller unit, a miniaturized 6 degrees-of-freedom inertial measurement unit (IMU) including a tri-axial accelerometer and gyroscope, a Bluetooth Low Energy (BTLE) communication module, and a rechargeable battery. The patient’s smartwatch has a dedicated mobile application installed, monitoring the level of adherence to wearing the boot and providing real-time alerts and behavioral feedback depending on daily patient adherence and activity. The clinician dashboard provides web services with cloud storage, which allows the care team to monitor activity and adherence remotely and in near real time.
This study examined the measure of adherence and non-adherence to wearing the Smart Boot and its influence on balance control, gait performance (i.e., step count), and user experience in healthy adults. The results suggest that the Smart Boot is reliable and accurate in remote monitoring adherence and non-adherence to wearing the offloading boot at a high sensitivity rate of 90.56%, specificity rate of 88.04%, and accuracy rate of 89.29%. The Smart Boot offers innovative remote patient monitoring solutions to offloading interventions, enabling real-time monitoring of activity, adherence, and non-adherence to wearing the boot. In addition, it provides a real-time alert for non-adherence and facilitates remote monitoring through cloud storage and web services.
Subsequently, an Ossur DH Powered by Sensoria was presented at the recent American Podiatric Medical Association conference by our strategic partners, Baylor College of Medicine and USC Keck school of medicine led by Dr. Bijan Najafi and Dr. David Armstrong, respectively. The objective was to propose the concept of a smart removable offloading system with reinforcement of adherence via smart watch dedicated app and custom algorithms as well as remote cloud-based monitoring for diabetic foot ulcer patients.
A subsequent study published in the prestigious sensors journal “Taking a Load Off: User Perceptions of Smart Offloading Walkers for Diabetic Foot Ulcers Using the Technology Model” concluded that smart offloading with a remote patient monitoring solution may help promote adherence among older adults to wear offloading boots prescribed for DFUs.
The design of the Defender walker that was used in this study, regardless of being irremovable or removable, was better accepted among people who identified as Hispanic or Latino. Further, findings suggest clinicians could provide additional patient education for people who report experiencing at least one fall over the previous 12 months, particularly in putting on and taking off the walker.
Lastly, at Sensoria we are grateful to have been awarded an R01 federal grant funded by National Institute of Health (NIH), National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney disease (1R01124789-01A1) with Baylor College of Medicine and USC Keck School of Medicine to continue to lead the charge in addressing diabetic foot ulcer complications, improving outcomes, enhancing quality of life, and help in reducing risk of amputation.
If you would like to learn more about the remote patient monitoring solution for diabetic foot ulcer patients, please visit: Diabetic Foot Ulcer Boot — Sensoria Health and Foot Defender+ – Defender Ops